How gig companies are lowering insurance costs with telematics

Gig economy companies have more drivers on the road than ever before. In 2023, two of the leading gig companies had over 7.4M drivers on American roadways combined. Analysts estimate that more than 50% of the U.S. workforce could be part of the U.S. gig economy in less than five years.
This trend collides with roads becoming riskier, as CMT’s data shows. With drivers spending 2 minutes and 12 seconds of every hour on the road distracted, it should be no surprise that 34% of crashes happen within a minute of distracted driving. With drivers focused on their phones instead of the road, many distracted driving crashes are more severe.
As a result, insurers saw a 40% and 50% increase in severity for bodily injury claims and vehicle damage claims from 2018 to 2022. The increase in severity is also attributed to rising labor and repair costs, medical inflation, and legal expenses.
As the number of severe crashes skyrockets, insurers are raising their annual premiums to offset the spike in claims. One top ten auto insurer’s annual premium written for Uber exceeded $684M in 2022, up from $338M in the previous year.
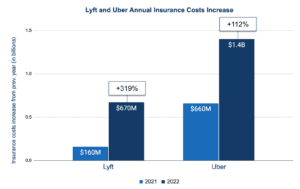
The result is that auto insurance has become the top expense for gig companies. In 2022, Uber’s insurance costs increased by $1.4B from 2021, contributing to a 110% increase in its cost of revenue. Lyft’s insurance costs increased by $670M, contributing to 91% of its increase in cost of revenue. Doordash’s cost of revenue grew by 59% to $975 million, also driven by insurance costs.
One way gig companies are reducing insurance expenses is by introducing telematics programs to improve driver safety. They’re running programs that provide their drivers with personalized driving insights and real-time coaching. By creating safer drivers, gig companies can reduce crash rates and insurance costs.
Insurers are encouraging gig companies to take this strategy. During Allstate’s 2022 Investor meeting, Allstate CEO, Tom Wilson explicitly called on gig companies to adopt telematics. This came after Allstate cut back on its transportation network company business after falling short of profit targets.
“We’ve probably written over $1 billion of premium in that business with the big transportation network companies, and it’s not meeting our profitability targets,” Wilson said. “So, we’re essentially exiting the business unless those carriers want to use telematics.”

So, how can telematics improve risky driving behaviors and lower annual premiums?
Gig companies that have run telematics programs have seen their riskiest drivers improve, which makes a big difference in their overall risk profile. CMT’s data shows that the riskiest 10% of drivers are 12X more likely to crash than the safest drivers.
Gig companies are seeing real results. One gig company ran a program that provided drivers with real-time alerts when drivers braked too hard. Hard braking is predictive of future crashes because it shows that drivers are avoiding potential collisions. Gig companies using real-time alerting are coaching their drivers to identify risky driving events, so they can prevent them in the future. In one program, hard brake alerts helped drivers drop hard braking by 30%, which can reduce crashes by 5%.

Personalized feedback and education helps drivers learn more about their risky behaviors. A CMT study of 10,000 drivers found that raising driver awareness around risky driving reduces distraction by 25%. Another study found that providing any driving feedback reduces hard braking by 15%. Generating engagement in these programs will be key for gig companies. Highly engaged drivers, those who open telematics apps and review their driving score weekly, are 65% safer than unengaged drivers.
Rewards is another strategy that engages drivers and reduces risk. Many gig companies have existing rewards programs based on completed trips, customer satisfaction, and on-time delivery. Drivers are earning incentives like 10% cash back on gas, store discounts, and more. Since these programs already exist today, gig companies can easily introduce a rewards structure based on safe driving insights. Another way to reward safe driving is allowing the safest drivers to get top priority on trips where they’re likely to earn the biggest tips. This type of safe driving reward ensures that the most active drivers on the gig companies’ platforms are also the safest.
The net effect of rewards programs is fewer crashes, which lowers claims costs for gig companies. CMT’s data shows that rewards reduce risky behaviors by up to 50%, dropping the likelihood of crashes and injuries by 5-10%.

For a gig economy company with 300,000 drivers, this could prevent up to 750 crashes. And with the average liability property damage claim averaging $5,300 recently, this could mean saving over $4M in claims costs alone.
Beyond minimizing claims costs by reducing crash risk, gig companies are exploring how to improve the efficiency of their claims operations with crash data. Knowing when a driver gets in a crash and its crash severity allows gig companies to resolve claims faster between themselves, drivers, and insurance carriers. The delays add up — a top carrier experienced $82M unfavorable development in its TNC business in 2022 because of the frequency of late-reported claims.
Allstate’s Tom Wilson seems to be getting his wish — many gig economy companies are already using telematics to reduce insurance costs by making drivers safer. As insurance costs continue to rise for gig economy companies, telematics could be the difference between success and failure.